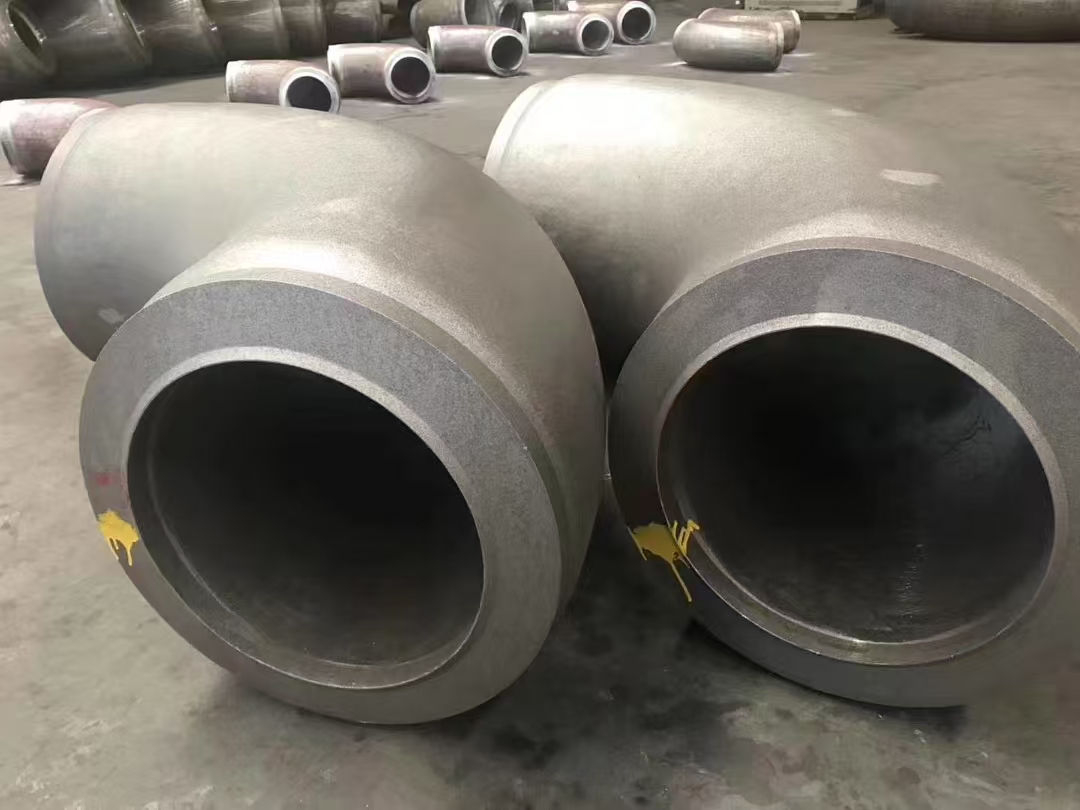
Martensitic stainless steel is a category of stainless steel that owes its name to the martensite phase, which is hard and brittle. This type of steel is distinguished by its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, making it an essential material in various industrial applications. Its unique combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance has cemented its place in sectors ranging from aerospace to heavy machinery.

1.Chemical Composition:
The chemical composition of martensitic stainless steel typically includes a high carbon content along with significant amounts of chromium, which is responsible for its stainless properties. It also contains other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and sometimes manganese, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen, which are added to enhance specific properties like toughness or improve corrosion resistance. The exact composition varies based on the grade and intended application.

2.Mechanical Properties:
Martensitic stainless steel is renowned for its high tensile and yield strength, along with good fatigue resistance. These properties make it ideal for components subjected to high stresses and cyclic loading. Furthermore, the material’s hardenability allows it to achieve high hardness values after appropriate heat treatment processes, including quenching and tempering. This results in a material that can withstand severe wear conditions while maintaining a decent level of ductility and notch toughness.

3.Application Fields:
Due to its robust characteristics, martensitic stainless steel finds extensive use in industries where both strength and corrosion resistance are paramount. It is commonly utilized in the manufacturing of cutting tools, valves, pumps, shafts, bolts, and other components requiring high mechanical strength and durability. The oil and gas industry relies on this steel for parts exposed to harsh chemicals and environments. Additionally, it is used in architectural applications and in the production of certain surgical instruments where sterilization resistance is crucial.
4.Company Advantages:
Companies specializing in martensitic stainless steel often boast advantages such as advanced metallurgical technology, precision engineering, and bespoke material solutions. They possess the capability to tailor the steel’s composition and properties to meet specific customer requirements. With stringent quality control measures and adherence to international standards, these companies ensure that the material delivered is of the highest quality. Moreover, their ability to offer comprehensive services from material selection to final fabrication contributes significantly to their competitive edge in the global market.
The manufacturing process of martensitic stainless steel includes steps such as **material selection, smelting, forging, heat treatment, and cold working. The details are as follows:
- Material Selection:
– Martensitic stainless steel requires appropriate raw materials, typically including alloy elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. These elements enhance the corrosion resistance and strength of stainless steel[^1^].
- Smelting:
– The selected raw materials are melted in an electric furnace or electric arc furnace to obtain the desired alloy solution. During the smelting process, the content of alloy elements and furnace temperature must be controlled to ensure the correct alloy composition[^1^].
- Forging:
– The molten alloy solution is cast or forged to achieve the desired shape and size. During forging, temperature and force must be controlled to ensure uniform microstructure and good mechanical properties[^1^].
- Heat Treatment:
– The forged stainless steel is heat-treated to form a martensitic structure. The temperature and duration of heat treatment must be determined based on the composition of the stainless steel and the desired properties[^1^].
- Cold Working:
– Cold working is performed on the heat-treated stainless steel to further enhance its strength. Methods of cold working include cold rolling, cold drawing, and cold heading. During this process, temperature and deformation must be controlled to ensure that the properties of the stainless steel are not compromised[^1^].
- Quality Inspection:
– The finished product must undergo quality inspection to ensure it meets standards and customer requirements. This includes testing the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of the stainless steel[^1^].
Conclusion:
Martensitic stainless steel continues to serve as a backbone material in many industries due to its superior mechanical performance and corrosion resistance. As technology advances and demands for more efficient materials increase, companies specializing in this type of steel are well-positioned to capitalize on their expertise and provide innovative solutions for emerging challenges in the ever-evolving landscape of industrial applications.