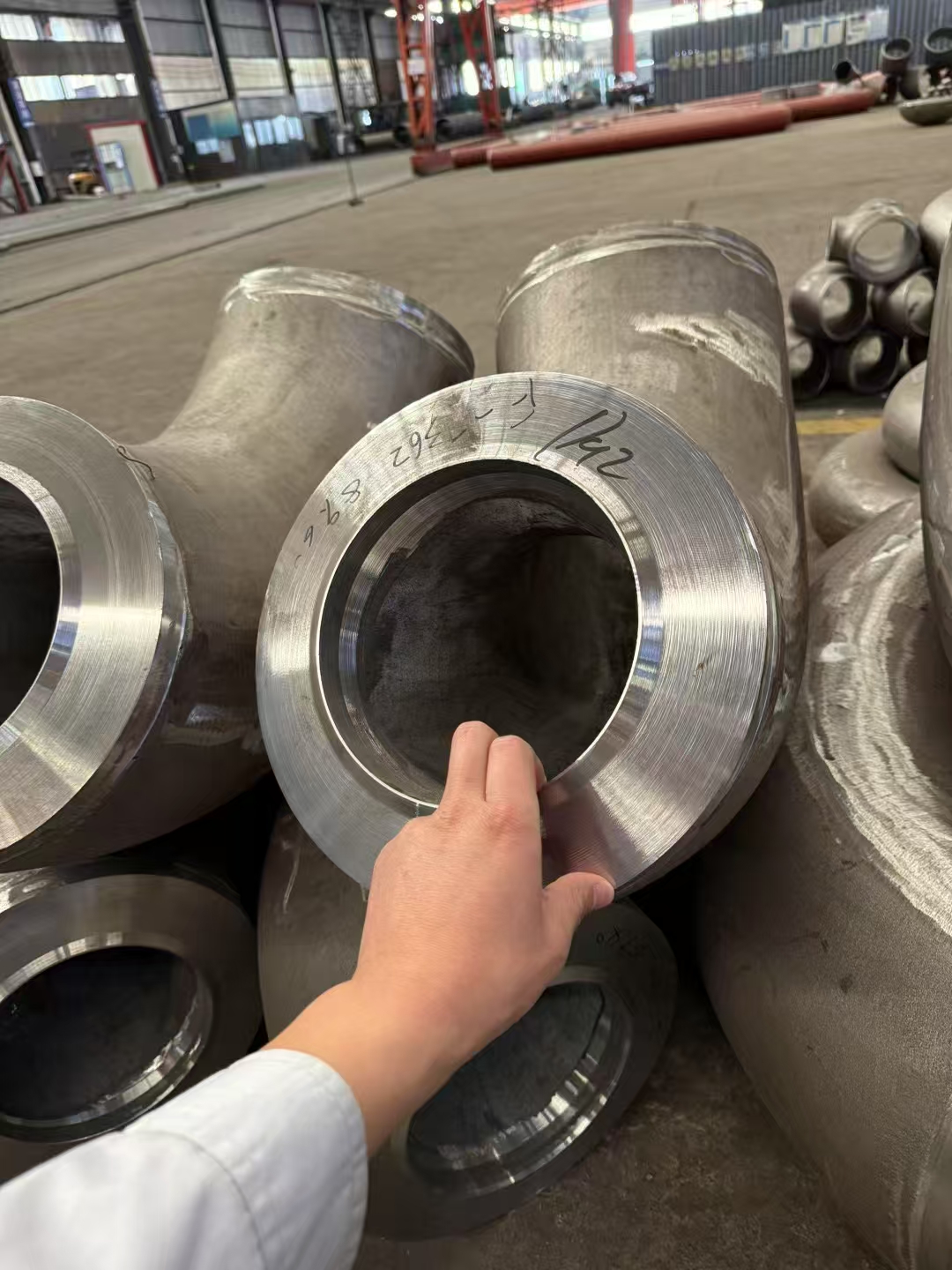
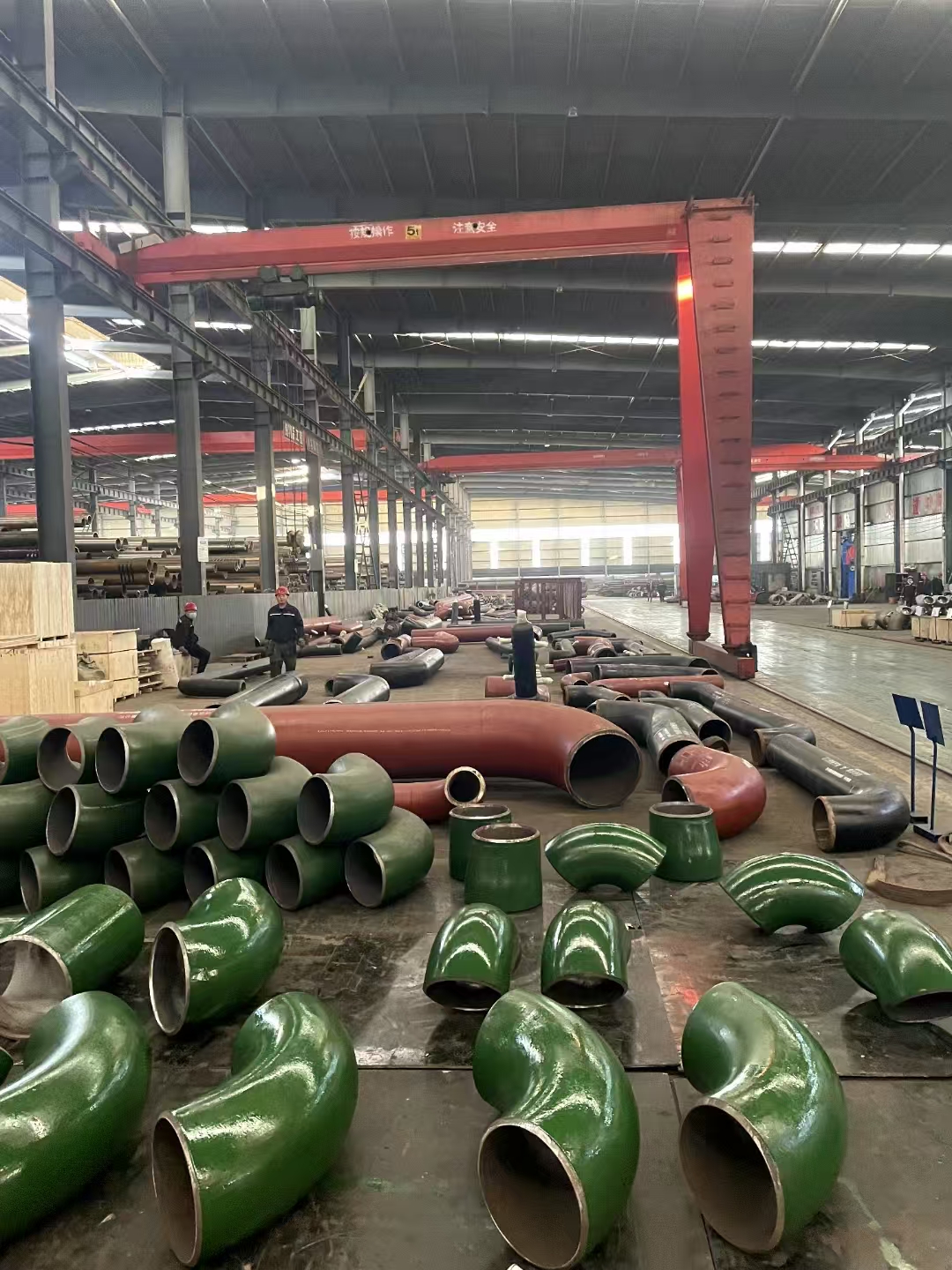
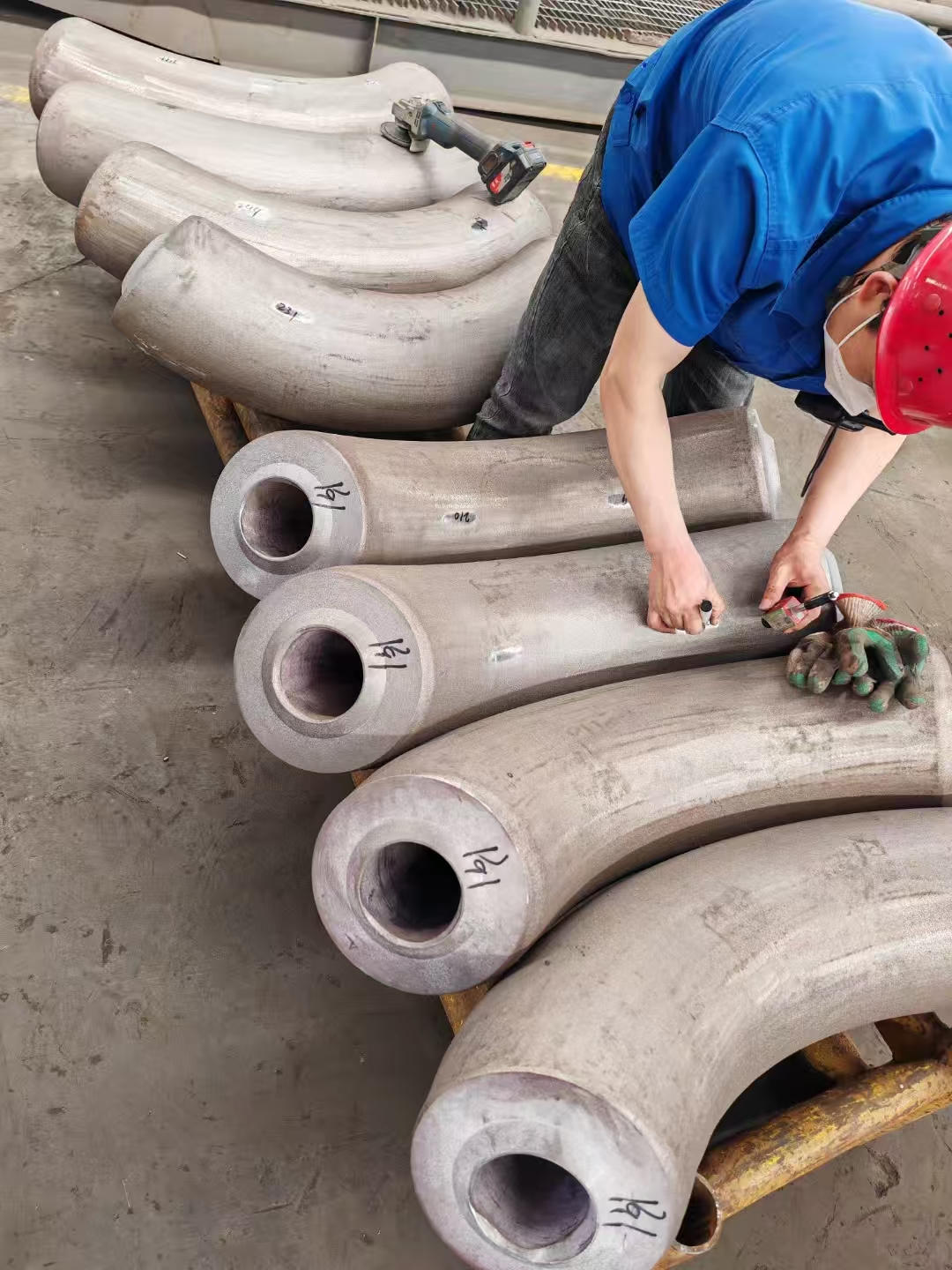
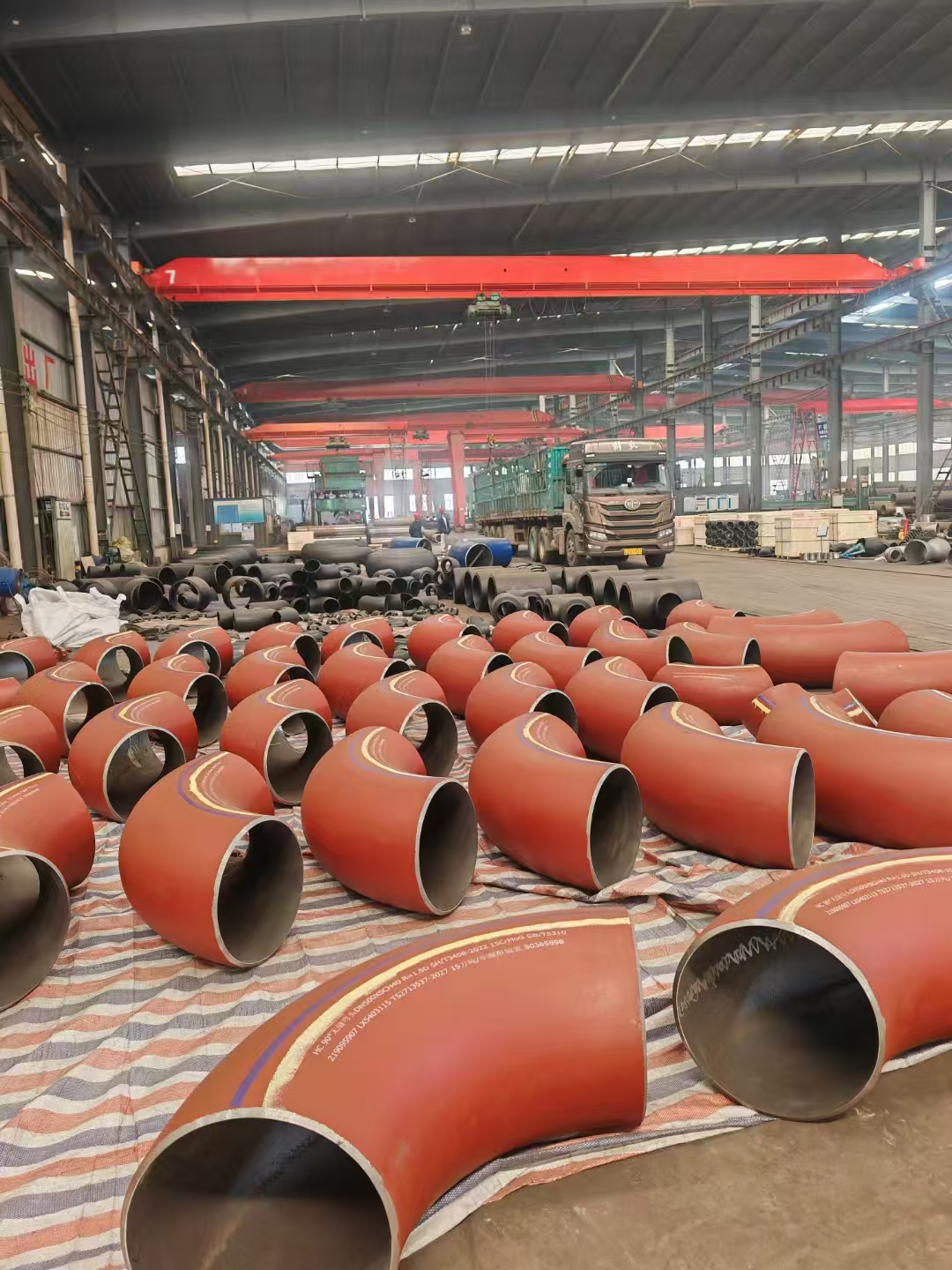
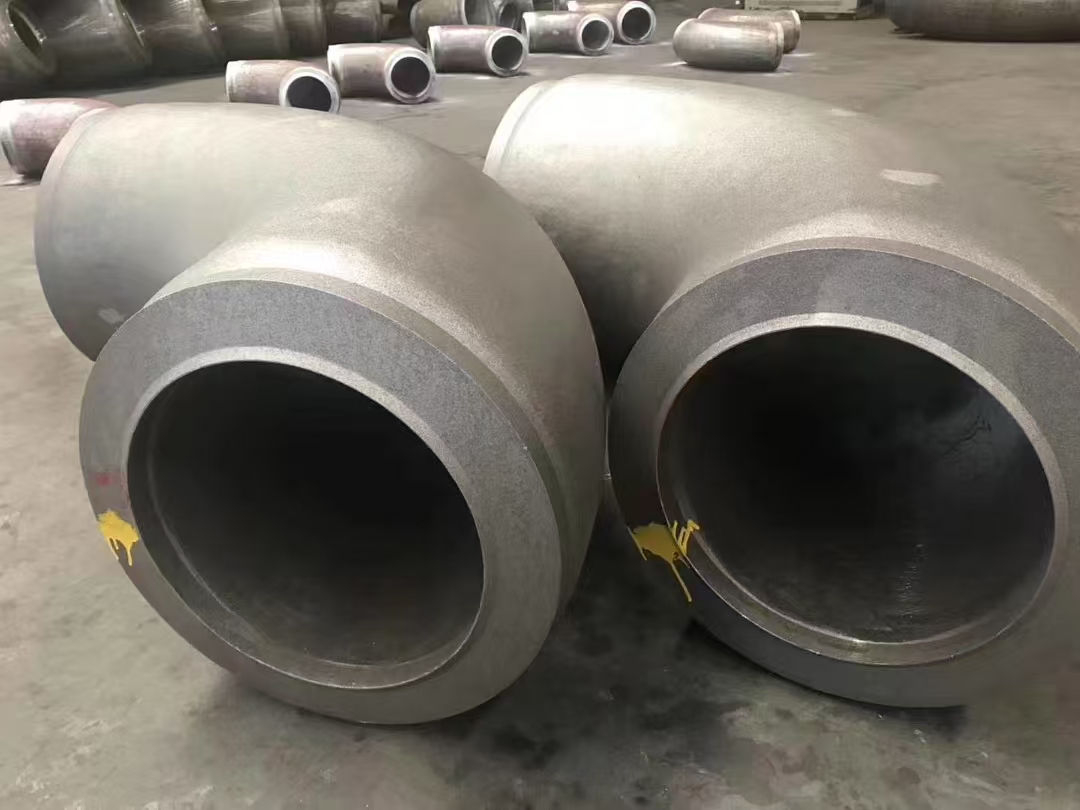
Austenitic stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321 is softened by solution treatment. Generally, the stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321 is heated to about 950~1150 ℃. After a period of heat preservation, the carbide and various alloy elements are fully and evenly dissolved in austenite, and then rapidly quenched and cooled. Carbon and other alloy elements can not precipitate in time to obtain pure austenite structure, which is called solution treatment.

The solution treatment of stainless steel flange has three functions.
1. The structure and composition of stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321 are uniform, which is especially important for raw materials, because the rolling temperature and cooling speed of each section of hot rolled wire rod are different, resulting in inconsistent structure.
Atomic activity intensifies at high temperatures, σ Phase dissolution, chemical composition tends to be uniform, and uniform single-phase structure is obtained after rapid cooling.
2. Eliminate the work hardening of stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321 to facilitate the continuous cold working.
Through solution treatment, the distorted lattice is restored, the elongated and broken grains are recrystallized, the internal stress is eliminated, the tensile strength of the steel pipe decreases, and the elongation increases.
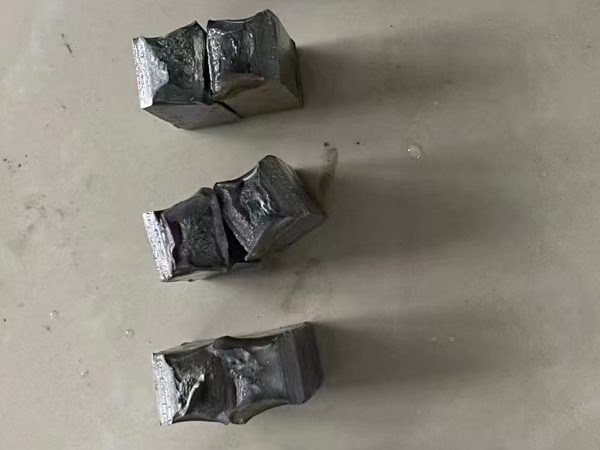

3. Restore the inherent corrosion resistance of stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321.
The corrosion resistance of stainless steel decreases due to carbide precipitation and lattice defects caused by cold working. After solution treatment, the corrosion resistance of steel pipe recovers to the best state.
For stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321, the three elements of solution treatment are temperature, holding time and cooling rate. The solution temperature is mainly determined according to the chemical composition.
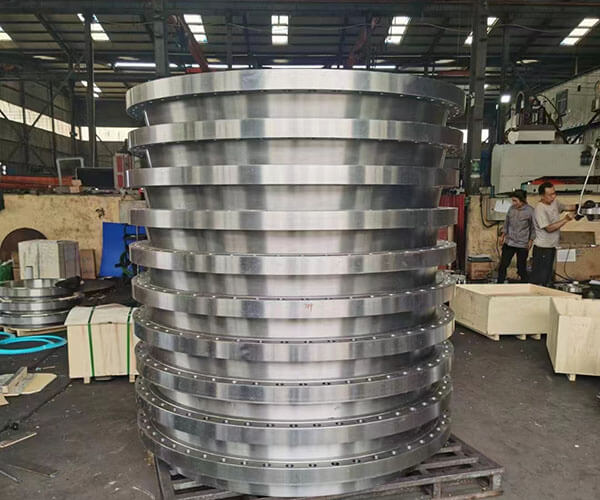

Generally speaking, the solution temperature of the grades with many kinds and high content of alloy elements should be increased accordingly. Especially for steel with high content of manganese, molybdenum, nickel and silicon, the softening effect can be achieved only by increasing the solution temperature and making it fully dissolved.
However, for stabilized steels, such as 1Cr18Ni9Ti, when the solution temperature is high, the carbides of stabilized elements are fully dissolved in austenite, which will precipitate at the grain boundary in the form of Cr23C6 during subsequent cooling, causing intergranular corrosion. In order to prevent the carbides (TiC and Nbc) of stabilized elements from decomposition and solution, the lower limit solution temperature is generally adopted.
As the saying goes, stainless steel flanges are not easy to rust. In fact, some stainless steel flanges have both rust resistance and acid resistance (corrosion resistance). The rust resistance and corrosion resistance of stainless steel flange F304L F316L F321 are due to the formation of chromium rich oxide film (passive film) on its surface. The rust resistance and corrosion resistance are relative.
The experiment shows that the corrosion resistance of steel in weak medium such as atmosphere, water and oxidizing medium such as nitric acid will increase with the increase of chromium content in steel, which is in direct proportion When the chromium content reaches a certain percentage, the corrosion resistance of steel will change suddenly, that is, from easy to difficult to rust, from non corrosion resistance to corrosion resistance.
Flange type for Stainless Steel Flange Solution